Your cart is currently empty!
CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN ADEQUACY CRITERIA
Published by
on
A summary of adequacy criteria for various cytology specimens.
Adequacy criteria: based on 2014 Bethesda system of reporting cervical cytology
- Satisfactory:
- Adequate number of well visualized or preserved squamous or squamous metaplastic cells
- Conventional smear: minimum 8,000 – 12,000 cells
- Liquid based preparation: minimum 5,000 cells
- Woman’s postchemotherapy, radiotherapy, postmenopausal, atrophic changes or posthysterectomy may have < 5,000 cells and be deemed adequate at laboratory’s discretion (if > 2,000 cells)
- Exception: adequate if any abnormal cells are present
- Unsatisfactory:
- More than 75% of cells obscured by inflammation, bacteria or interfering substances (lubricants and blood)
- 50 – 75% of cells obscured, include a disclaimer describing how and the percentage of cells obscured

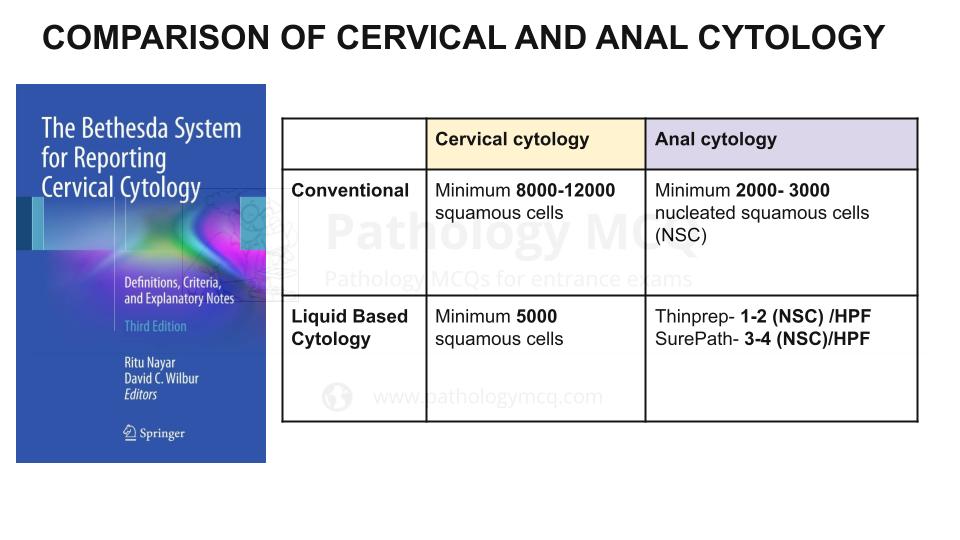
Specimen adequacy is based primarily upon specimen cellularity and morphological quality of the sample.
As outlined in The Bethesda System,
A minimum cellularity for conventional anal-rectal cytology smears is 2,000 to 3,000 nucleated squamous cells (image) for conventional smears,
1–2 nucleated squamous cells per high power field (hpf) for ThinPrep specimens, and 3–6 nucleated squamous cells per hpf for SurePath specimens.
Specimens composed primarily of anucleate squamous cells and specimens that do not meet minimum criteria for cellularity should be considered unsatisfactory for evaluation; provided that no abnormal cells are identified, no diagnostic interpretation/result should be rendered for such specimens.
Obscuring factors such as fecal material, bacteria, and inflammation may hinder evaluation, and when the majority of nucleate squamous cells are obscured, specimens should be considered unsatisfactory for evaluation.
While the presence of a transformation zone component is not required for a satisfactory specimen, presence or absence of glandular columnar cells should be noted.

3. FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF THYROID NODULES
Adequacy criteria based on The Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology 2017 2nd edition.
FNA smear should contain ≥ 6 groups of well visualized follicular cells (≥ 10 cells/group), preferably on a single slide
Exceptions (a minimum number of follicular cells is not required)
✅Solid nodules with cytologic atypia, which qualify into categories III – VI
✅Solid nodules with inflammation are considered benign
✅Only numerous inflammatory cells
✅Lymphocytic thyroiditis, thyroid abscess or granulomatous thyroiditis
✅Nodules with abundant colloid are placed in the benign category even in the absence of follicular epithelium

According to The Paris System for Reporting Urinary Cytology
Voided urine: >30 ml without non-urothelial features obscuring urothelial morphology
Instrumented urine: 2600 cells or at least 20 cells in 10 HPF may be taken as adequacy criteria.
According to The Milan System for Reporting Salivary Gland Cytopathology (MSRSGC) : More than 60 lesional cells are required for a cytologic diagnosis.
Any atypical cells or sign of features such as mucin is also considered adequate.
6. PANCREATICO-BILIARY CYTOLOGY
According to The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology (PSC) developed in 2014
Contains adequate cellular or extracellular tissue to evaluate or define a lesion that is identified on imaging
Only GI contamination, or benign pancreatic tissue indicates missed lesion and is considered non diagnostic.
NOTE: MUCIN is considered adequate in MILAN( Salivary gland cytology) but not in pancreatico-biliary cytology.
According to The international system standardized reporting of serous fluid cytology
Volume of fluid: There is no specific cutoff but volume >50 mL to 75ml is considered adequate
Cellularity: There is no definitive criteria of number of mesothelial cells for adequacy and the criteria might vary depending on the pathologic process.
Quality of preparation: poor cell preservation, degeneration, hemorrhage, artifacts and contaminants can impair interpretation and is considered inadequate,
Presence of alveolar macrophages are a must for sputum cytology specimens to be deemed adequate
9. FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY OF BREAST
✅No definite criteria for adequacy in breast FNA cytology
✅MD Anderson Cancer Center Group proposed that 4 – 6 well visualized cell groups with 10 or more cells / flat sheets as an adequacy criteria.
✅Samples that lack epithelial cells are considered inadequate in general
✅If the lesion is suspected to be lipoma or fat necrosis, the absence of epithelial clusters doesn’t indicate inadequacy
10. FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION BIOPSY OF BREAST
According to Yokohama system for reporting Fine needle aspiration biopsy
✅If there is a mass lesion on palpation or imaging, which does not decrease in size on FNAB, the presence of seven tissue fragments, each of 20 or more epithelial cells, are suggested as a measure of adequacy.
11. SUMMARY OF CYTOLOGIC ADEQUACY CRITERIA- ALL SPECIMENS

- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/625
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/626
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/627
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/628
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/629
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/5824
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/5796
- https://t.me/pathologymcqs/5832
JOIN our TELEGRAM and WhatsApp group for daily MCQs
We post MCQs on social media daily- FOLLOW OUR SOCIAL MEDIA PAGES
Any additions and comments are welcome
References;
OUR COURSES/E-BOOKS

Courses:
Learn more >

Learn more >

E-Books in amazon kindle:
Learn more >
Leave a Reply